
Custom Online 3D Printing Service
Our 3D printing service delivers custom, high-quality parts with complex designs and precision. Upload your files, choose materials and finishes, get instant quotes, and enjoy fast turnaround—ideal for prototypes, small batches, and unique components.
- Competitive FDM, SLA, SLS, MJF Services
- Cost-Effective 3D Printing Solutions
- Rapid Prototyping
Trusted by






Professional Team
Our professional team delivers exceptional expertise and dedication to meet all your project needs.

One-Stop Service
One-stop service from prototyping to finishing, streamlining your sourcing process.

Top Quality
We provide high-quality 3D printing services with precision, durability, and exceptional craftsmanship.

Fast Delivery
Enjoy fast delivery with Witcool, ensuring your orders arrive quickly and efficiently every time.

Low Cost
We offer low-cost 3D-Printing services with guaranteed precision, quality, and reliable delivery.
What is 3D Printing
The process of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, convert computer blueprints into three-dimensional objects. Unlike traditional processes that remove material, 3D printing adds layers by layer. A digital 3D model is first created in CAD software and then split into horizontal layers.
The printer creates the final shape gradually using materials such as resin, metal, or plastic. This technology allows for precise features and complicated geometries that would be difficult or expensive to create using standard methods.
3D printing is extensively used in industries such as consumer items, automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. It manufactures lightweight aviation parts, medical implants, and specialised automobile components and prototypes. It specialises in rapid prototyping, allowing developers to swiftly iterate and test concepts.
3D printing promotes creativity by allowing for small-batch production, bespoke manufacturing, and quick product development. It is both efficient and adaptable.
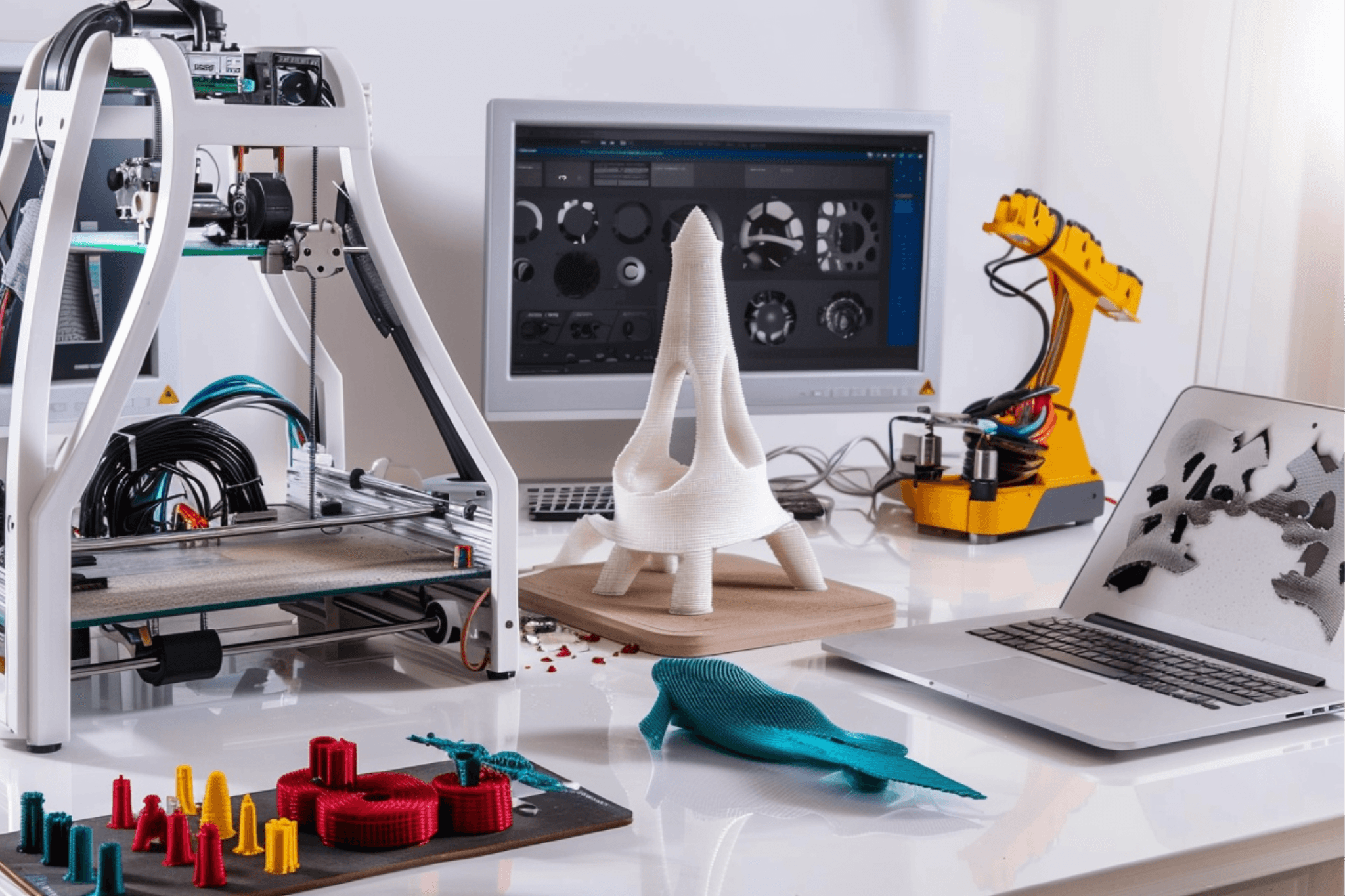
Our 3D Printing Capabilities
Explore the possibilities of 3D printing with Witcool and experience the future of manufacturing today.
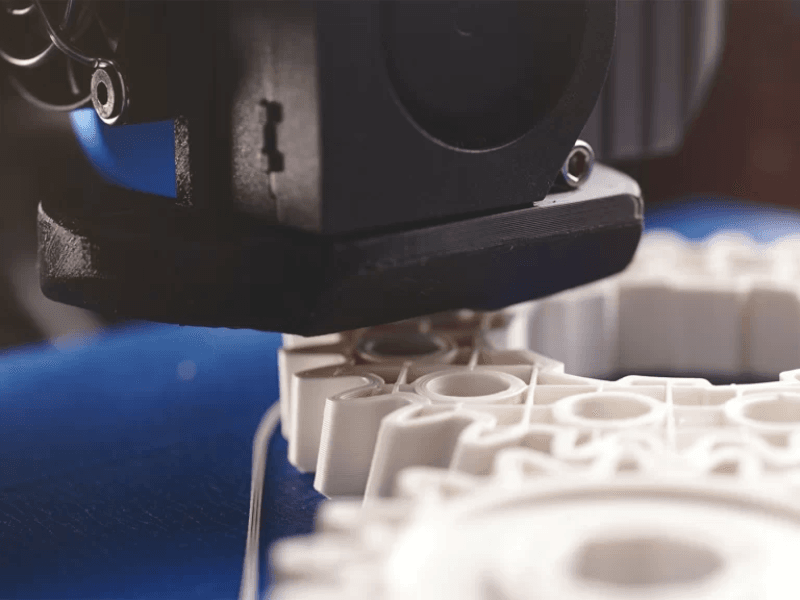
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a popular 3D printing technology that extrudes thermoplastic filaments layer by layer to create objects. The process begins with a digital model sliced into layers, guiding the printer’s nozzle as it deposits melted filament along a predefined path. As each layer cools and hardens, the next layer is added until the object is complete.
FDM is valued for its affordability, versatility with various thermoplastics like PLA and ABS, and suitability for functional prototypes, concept models, and manufacturing aids. Its accessibility and capability to produce robust, dimensionally accurate parts make it widely used across industries.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powders into a solid, three-dimensional object. Unlike other methods, SLS does not require support structures, as unused powder acts as a self-supporting material during printing. This makes it ideal for creating intricate geometries and functional prototypes.
SLS is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare for producing parts with high strength, durability, and thermal resistance. Its versatility and ability to work with various materials make it a preferred choice for rapid manufacturing and custom production.
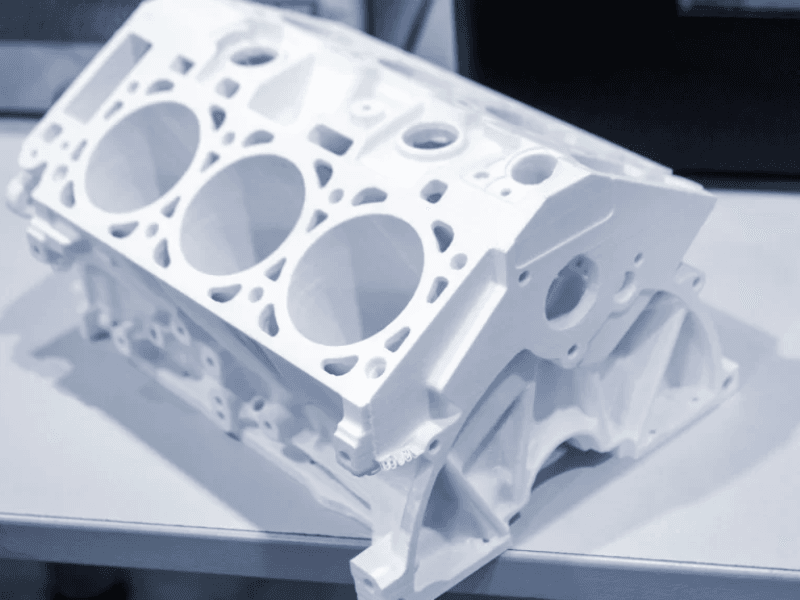
MJF (Multi Jet Fusion)
MJF (Multi Jet Fusion) is an advanced 3D printing technology known for its speed and accuracy in producing functional parts. It works by selectively applying fusing and detailing agents onto a bed of powdered material, which is then fused together by intense infrared energy. This process allows for high-resolution printing of intricate geometries with strong mechanical properties.
MJF is particularly valued for its ability to create durable end-use parts quickly, making it suitable for industries requiring rapid prototyping and production of complex components, such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
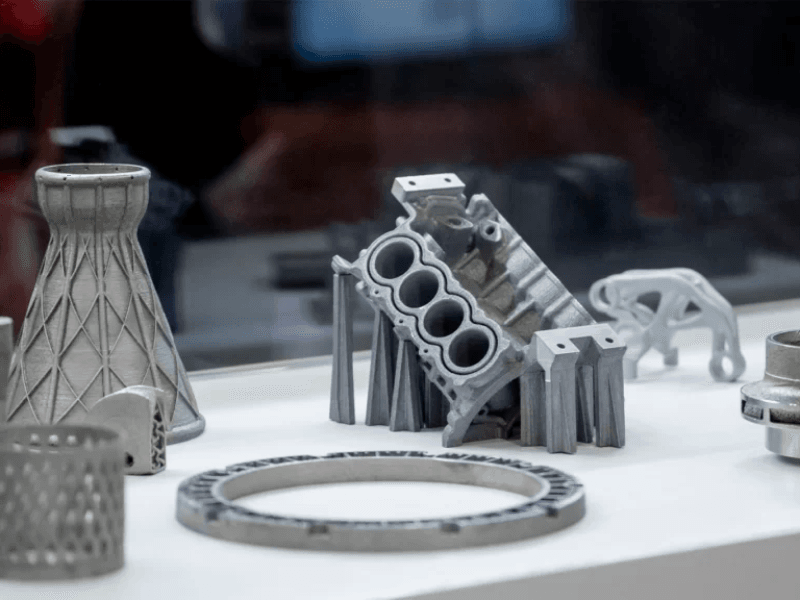
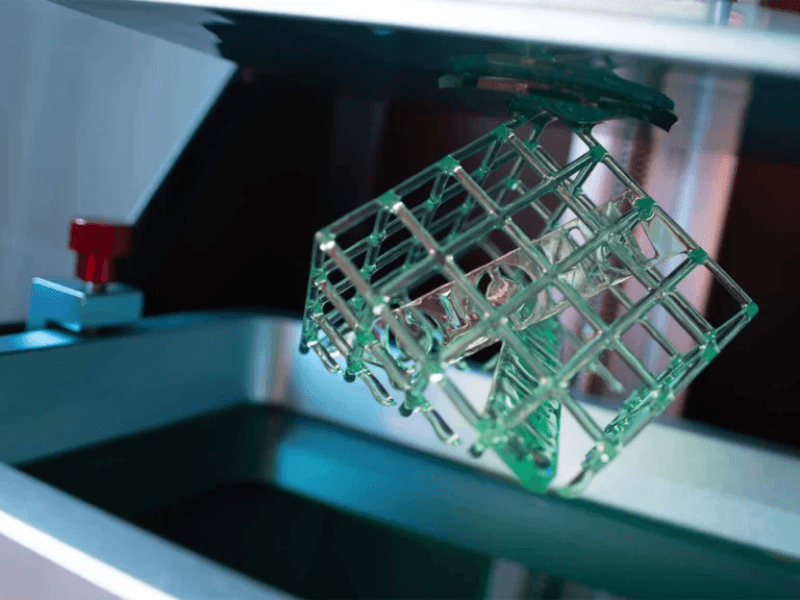
SLA (Stereolithography)
SLA (Stereolithography) is an additive manufacturing process where a laser selectively solidifies layers of liquid resin to create intricate 3D objects. It begins with a digital model sliced into cross-sectional layers. The SLA printer then uses a UV laser to trace each layer onto the liquid resin, causing it to solidify. This process repeats layer by layer until the entire object is formed.
SLA is known for its ability to produce highly detailed parts with smooth surface finishes and tight tolerances, making it suitable for applications in industries like prototyping, jewelry, and medical devices where precision and aesthetic quality are crucial.
Why Choose Us for 3D Printing Services
Explore the possibilities of 3D printing with Witcool and experience the future of manufacturing today.
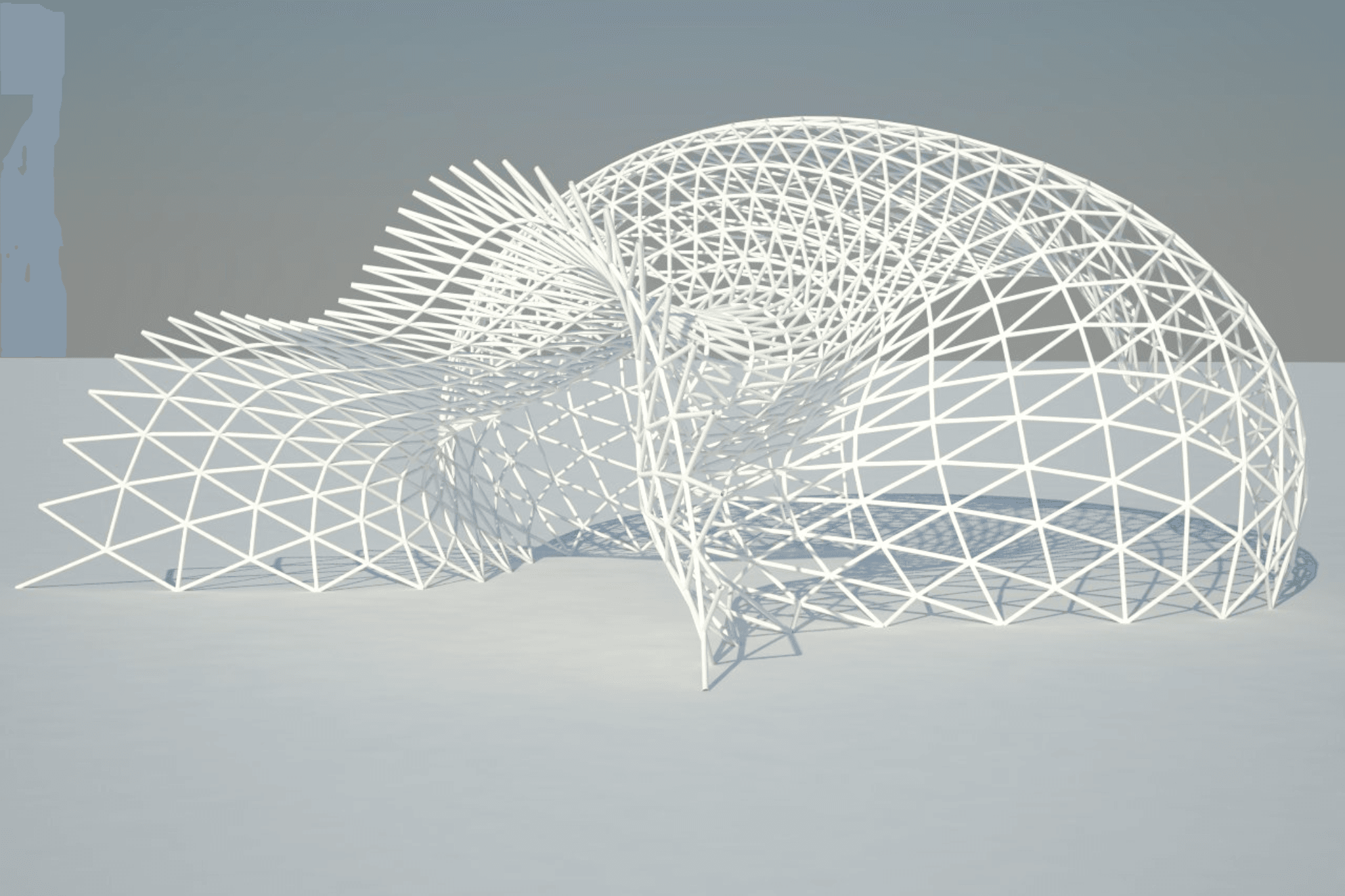
Design Flexibility & Complexity
3D printing offers unparalleled design flexibility, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and intricate details that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability enables innovative design solutions and supports the production of highly customized parts.
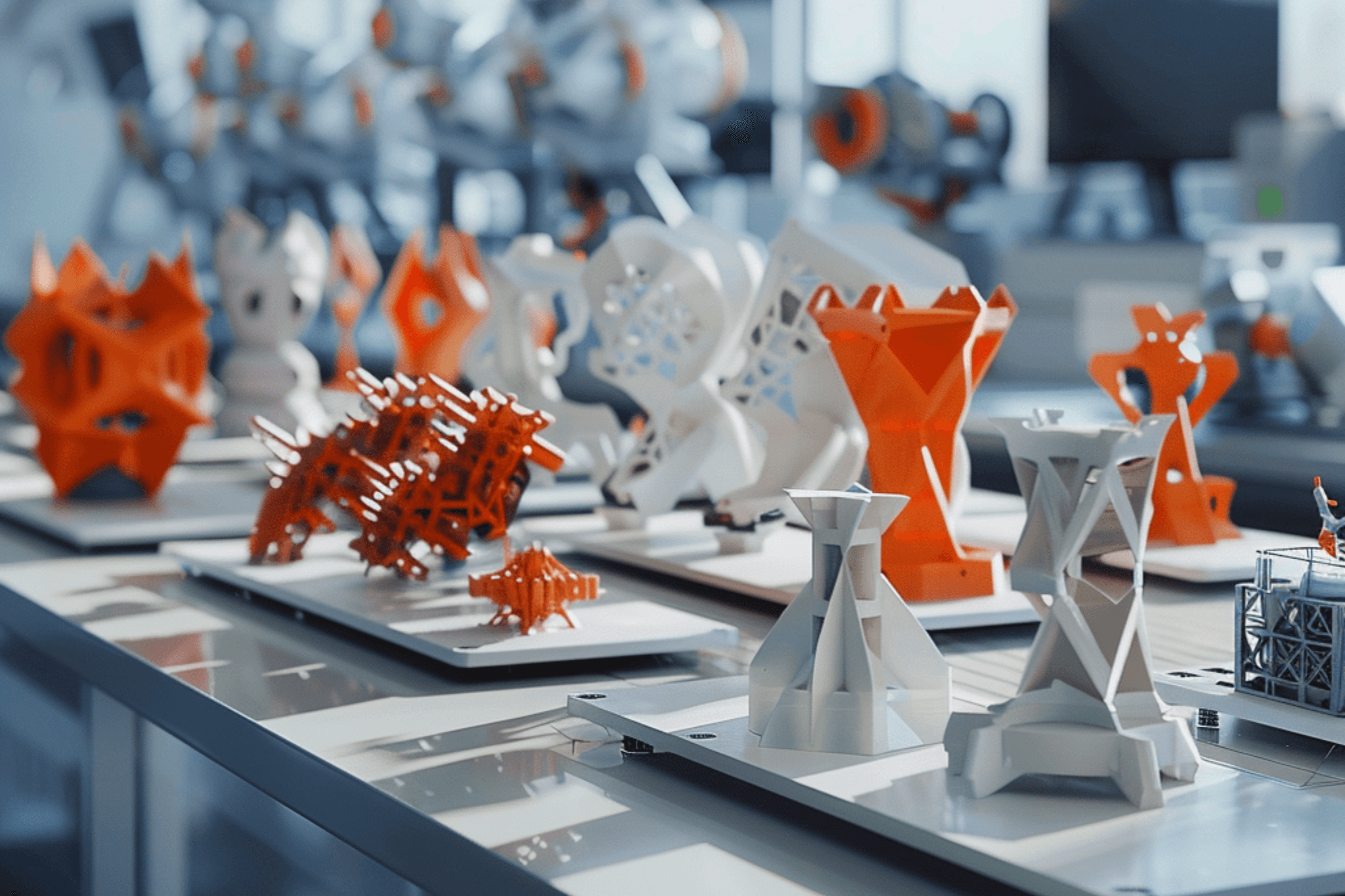

Rapid Prototyping & Iteration
3D printing significantly reduces the time required to develop and test prototypes. With the ability to quickly produce and modify designs, this technology accelerates the product development cycle, allowing for faster iterations and time-to-market.
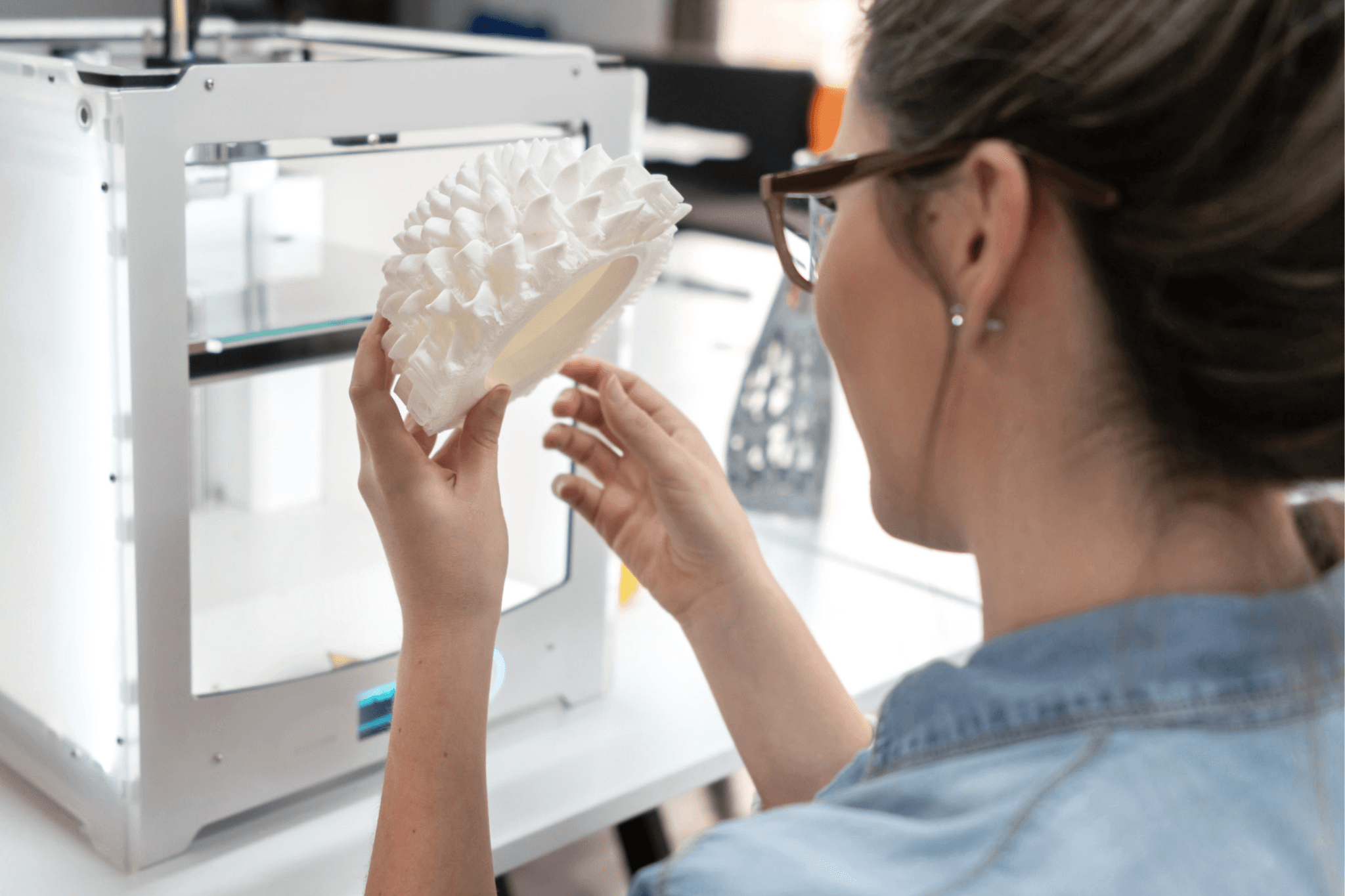

Reduced Waste & Cost Efficiency
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, which means material is only used where needed, minimizing waste. This efficiency translates into cost savings on materials and makes 3D printing an environmentally friendly option for producing complex parts with minimal excess.
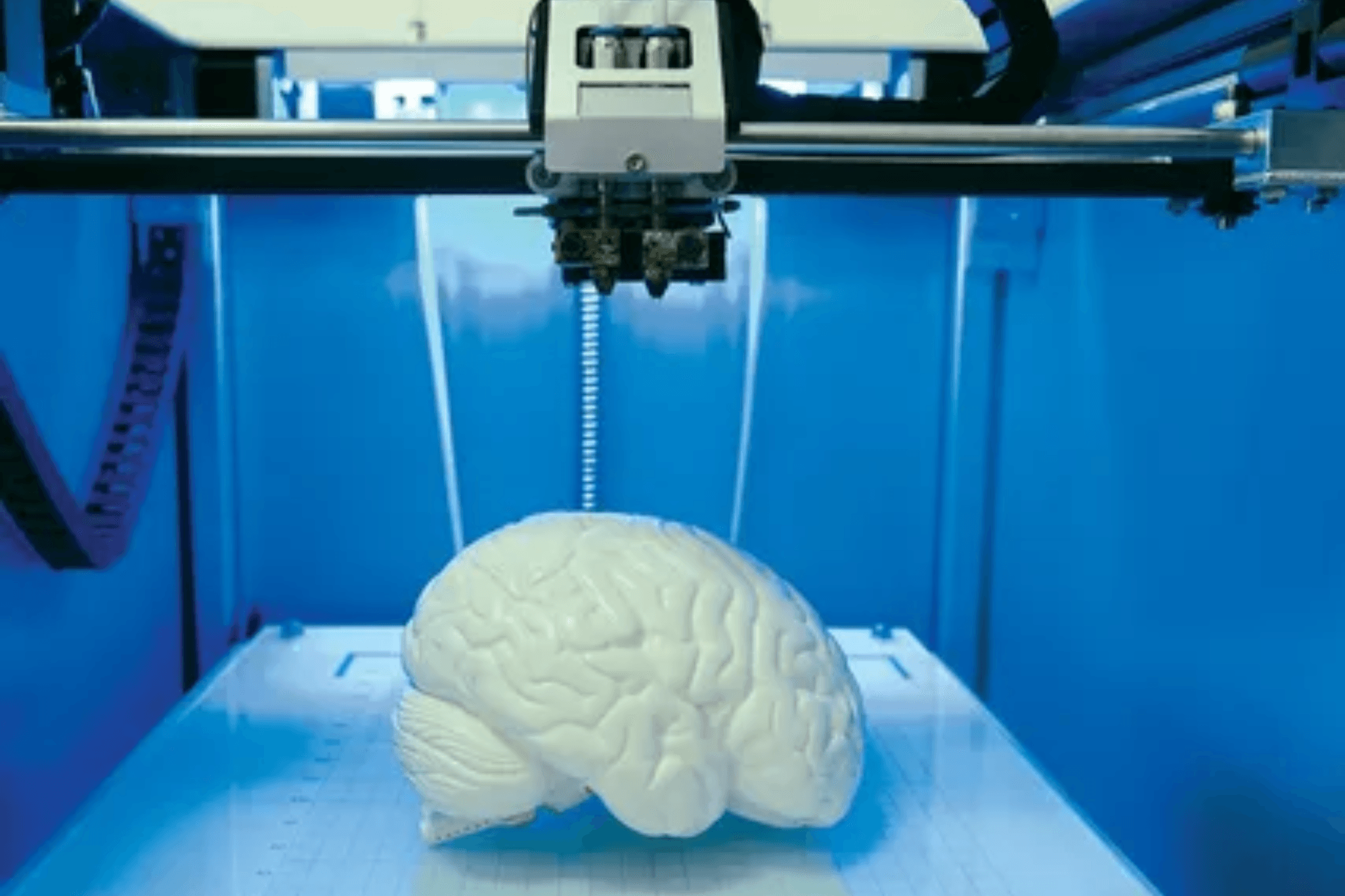

On-Demand Production & Customization
3D printing enables on-demand production, eliminating the need for large inventories and allowing for the creation of custom parts as needed. This flexibility supports just-in-time manufacturing and ensures that specific requirements can be met quickly and efficiently.
3D Printing Material
Explore a wide range of materials, including plastics, resins, metals, and composites, each offering unique properties to meet your project’s needs for strength, flexibility, precision, and aesthetic appeal.

Plastics
Our 3D printing materials include high-quality plastics like ABS, PLA, Nylon, and PETG, each offering unique benefits for various applications. ABS is robust and ideal for durable prototypes and end-use parts, while PLA is biodegradable and perfect for prototyping and educational projects. Nylon is known for its exceptional strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for industrial components, and PETG combines ease of printing with excellent durability and chemical resistance, ideal for strong, functional parts and protective components.
Metals
Our 3D printing materials feature premium metals such as Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Titaniuml, each offering unique benefits for various applications. Stainless Steel provides excellent strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for durable and long-lasting parts. Aluminum is lightweight with excellent mechanical properties, perfect for aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. Titanium offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, making it suitable for medical implants and high-performance engineering components.
Composites
Our 3D printing materials include advanced composite materials, offering superior strength, durability, and flexibility for various high-performance applications. These materials combine the best properties of different substances to create parts that are lightweight yet incredibly strong. Ideal for aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications, composite materials enhance product performance and longevity. Their exceptional thermal and chemical resistance makes them perfect for challenging environments, ensuring reliability and efficiency in every print.
3D Printing Surface Roughness
Understand how layer height, printing technology, and post-processing affect the texture and smoothness of 3D-printed parts, ensuring optimal performance, aesthetics, and fit for your specific application.
-
Printing Type Material
Post-Printing Roughness
Post-Processing Technology
Roughness After Processing
SLA
Photopolymer Resin
Ra 6.3
Polishing, plating
Ra3.2
MJF
Nylon
Ra 6.3
Polishing, plating
Ra3.2
SLS
White Nylon, Black Nylon, Glass-filled Nylon
Ra6.3-Ra12.5
Polishing, plating
Ra6.3
SLM
Aluminum Alloy
Ra6.3-Ra12.5
Polishing, plating
Ra6.3
SL
Stainless Steel
Ra6.3-Ra12.5
Polishing, plating
Ra6.3
Witcool 3D Printing Capabilities
Delivering precise, high-quality parts with complex geometries using advanced technologies and diverse materials, ideal for prototypes, small batches, and custom solutions across multiple industries.
-
Min. Wall Thickness
Layer Height
Max. Build Size
Dimension Tolerance
Standard Lead Time
SLA
0.6mm for unsupported walls, 0.4mm for supported walls on both sides
25 µm – 100µm
1400x700x500mm
±0.2mm (For >100mm, apply 0.15%)
4 Workdays
MJF
At least 1mm thick; avoid overly thick walls
Around 80µm
264x343x348mm
±0.2mm (For >100mm, apply 0.25%)
5 Workdays
SLS
From 0.7mm (PA 12) to 2.0mm (carbon-filled polyamide)
100–120 microns
380x280x380mm
± 0.3mm (For >100mm, apply 0.35%)
6 Workdays
SLM
0.8 mm
30μm – 50μm
320x320x400mm
±0.2mm (For >100mm, apply 0.25%)
6 Workdays
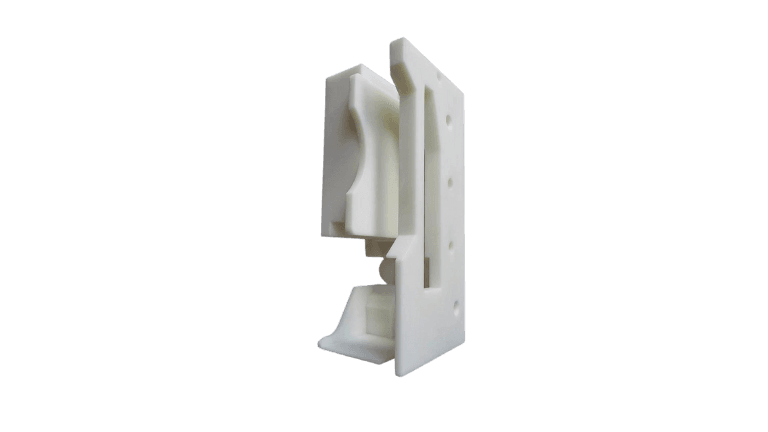
PART STUDY
3D Printing Clamp
Material: White ABS
Surface Treatment: NONE
Qty: 1Pc
Application: This 3D printed clamp is used in the medical industry for assembling diagnostic devices. Its robust construction and precise dimensions ensure reliable performance in critical medical applications, making it ideal for holding components securely during the assembly process. The use of white ABS provides excellent strength and durability, essential for maintaining high standards in medical device manufacturing.
Questions & Answers
At Witcool, we maintain strict control over every stage of the 3D Printing process, ensuring high product quality and precision. We deliver reliable solutions by adhering to standards and implementing innovations to enhance every project.
How does 3D printing work?
The digital model is sliced into layers, and the printer deposits material sequentially—melting or curing—to build the object from the bottom up.
What are the most common types of 3D printing technologies?
Common processes include FDM (FFF), SLA, SLS, DLP, MJF, and DMLS/EBM, each suited for different materials and precision levels.
What materials can be used?
Printers commonly use PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, Nylon, polycarbonate, resins, and even metals, ceramics, or bio-materials.
STL file format: what is it and why is it used?
The STL format, developed in 1987, encodes the object’s surface geometry using triangles and remains the most widely accepted format for slicing and printing.
What are the key advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing?
Advantages: custom geometries, reduced material waste, rapid prototyping, manufacturing flexibility.
Disadvantages: slower for large parts, size constraints, limited scalability, high cost for some processes.
Which industries use 3D printing the most?
It’s used in aerospace, automotive, medicine, education, architecture, consumer products, and defense, especially for prototyping and custom parts.


